PIB, September 12, 2024: A new method of introducing controlled defects in MOF-based supercapacitors through laser irradiation can help enhance the performance of existing energy storage technologies.
In recent years, several methods have been investigated for creating defects, such as thermal annealing, chemical exposure, high-energy ball milling, e-beam, and chemical vapor deposition. However, the extent of defects could not be controlled in the materials using these methods. Traditional methods lack the precision needed for fine-tuning of defects.
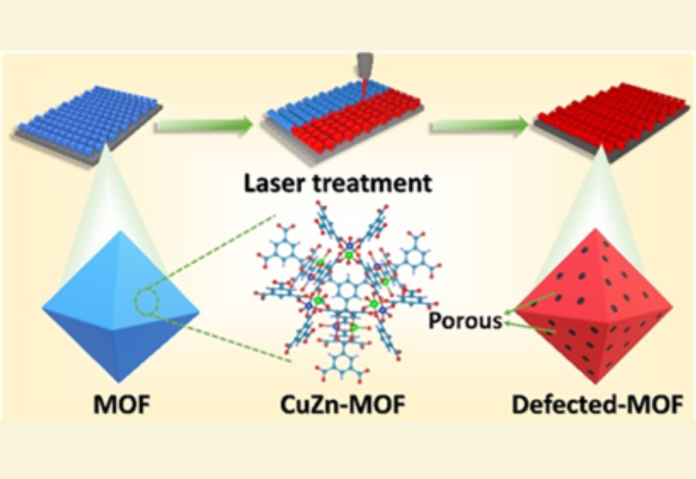
In order to enhance the activity of the pristine MOF (Metal Organic Framework) without transforming it into other materials or creating a composite out of it, scientists at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology, carefully adjusted laser power to systematically regulate defects and porosity, resulting in a significant increase in the electrode’s surface area and activity.
By precise tuning of the laser powers, Prof. Vivek Bagchi and his team controlled the defects and porosity in a pristine CuZn-BTC MOF without changing its crystal structure.
The novelty of this technique is that the crystallinity of the MOF material is mostly preserved; however, the laser irradiation enhances the activity of the material.
According to the researchers, upon exposure to laser radiation, some bonds in CuZn-MOF may rupture; however, the crystal structure remains intact as it is bound to several surrounding atoms. As a result, the three-dimensional (3-D) structure of MOF may develop pores throughout, potentially capturing multiple nano-sized MOF specks. These pores provide a microchannel pathway for ion diffusion. This 3-D porous network not only increases the stability but also enhances its accessibility to ions. The MOF nanoscooplets, upon elimination, also become integrated into the system, enhancing the overall surface area.
Laser processes are quicker than traditional methods, saving time; each step of the synthesis can be precisely controlled; and it is a safe, clean, and environmentally friendly approach, typically requiring no chemical solvents or extra materials.
This technique published in the journal ACS Materials Letter presents an opportunity for further research, particularly if applied to various other MOFs. However, using this approach to enhance the activity of existing technologies where MOF materials are used could lead to a significant technological advancement.
Also read: Unveiling the Ethical Imperatives: Navigating the Intersection of AI and Cybersecurity
Do Follow: CIO News LinkedIn Account | CIO News Facebook | CIO News Youtube | CIO News Twitter
About us:
CIO News is the premier platform dedicated to delivering the latest news, updates, and insights from the CIO industry. As a trusted source in the technology and IT sector, we provide a comprehensive resource for executives and professionals seeking to stay informed and ahead of the curve. With a focus on cutting-edge developments and trends, CIO News serves as your go-to destination for staying abreast of the rapidly evolving landscape of technology and IT. Founded in June 2020, CIO News has rapidly evolved with ambitious growth plans to expand globally, targeting markets in the Middle East & Africa, ASEAN, USA, and the UK.
CIO News is a proprietary of Mercadeo Multiventures Pvt Ltd.