The threats mobile devices are facing are real and evolving, and it is high time that an organization adopts robust security measures after understanding the evolving threat landscape.
This is an exclusive article series conducted by the Editor Team of CIO News with Kavitha Srinivasulu, Global Head – Cyber Risk & Data Privacy: R&C BFSI – Tata Consultancy Services (TCS).
As we step into the digital era and as technology is evolving day by day, our reliance on mobile devices has reached unprecedented levels. Mobile devices have become one of the daily essentials that act as the central hubs for our personal and professional lives. From managing finances, balancing work, and making online purchases to controlling smart home devices, mobile phones play a crucial role in our day-to-day activities. However, this increasing dependency has opened a big door for cybercriminals to hunt for data and create cyberthreats. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their approaches and targeting mobile devices with more sophistication.
As mobile devices allow us to do everything online with limited dependencies and challenges, it has become an easy communication tool in virtual marketplaces for online banking, shopping, controlling home appliances, and much more. While mobile phones may have made our lives easier and more convenient, there has also been a rapid increase in mobile threats, which calls for new mobile app security standards and measures to protect the data within the mobile devices. Securing applications and data against exploitation is the key focus for most companies, as most of the official applications are enabled on mobile devices for ease of use and scalability. The key responsibility of an organization is to secure applications and data against exploitation, whether they are stored on a system, laptop, or mobile device. Regardless of whether a mobile app is developed by a small or large company, cybersecurity is of utmost importance to keep all users’s data protected and out of reach of predators. Some of the current challenges and emerging threats are:
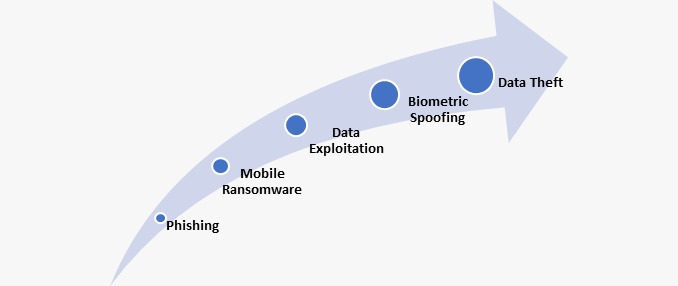
In 2024, the types of cyber threats targeting mobile devices will be broader and more dangerous. Predators are developing various vulnerabilities in mobile operating systems and apps, making the use of mobile devices more complicated. Concerns are raised about data exploitation on both personal and official applications managed using mobile devices. In mobile apps, the data within the app may be at risk if an organization fails to consider security measures during the app design itself to ensure the data protection of the end users. So, developers must be more vigilant while developing apps for both Android and iOS platforms. Securing mobile devices requires a multi-layered approach and investment in enterprise security solutions to safeguard the network. While there are key elements to mobile device security, each organization needs to find what suits best for its network and invest in the right security controls to build a robust cyber security posture.
User data is like a ransom for cybercriminals, as they can have access to anything from personal details to credit card details, including email passwords and user contact lists. Some of the individuals have also been fiddled into downloading malicious adware, and at times, they unknowingly subscribe to fake or fraudulently paid services. Therefore, a lapse in any mobile app’s security is a challenging scenario for app owners, developers, and end users. According to a recent survey, more than 60% of companies reported that an insecure mobile app caused a data breach, and 33% of them were without security controls in place to secure their app against further potential cyber-attacks or ransomware attacks.
A comprehensive mobile strategy is required that involves not just strategic planning but also identifies and mitigates roadblocks on the path to mobile project development, establishes strategic objectives and KPIs, and chooses the right security tools and technology. Security plays a vital role in using mobile apps, so it’s crucial to use best practices in protecting mobile apps against emerging risks and vulnerabilities growing with the technology.
Some of the best practices include:
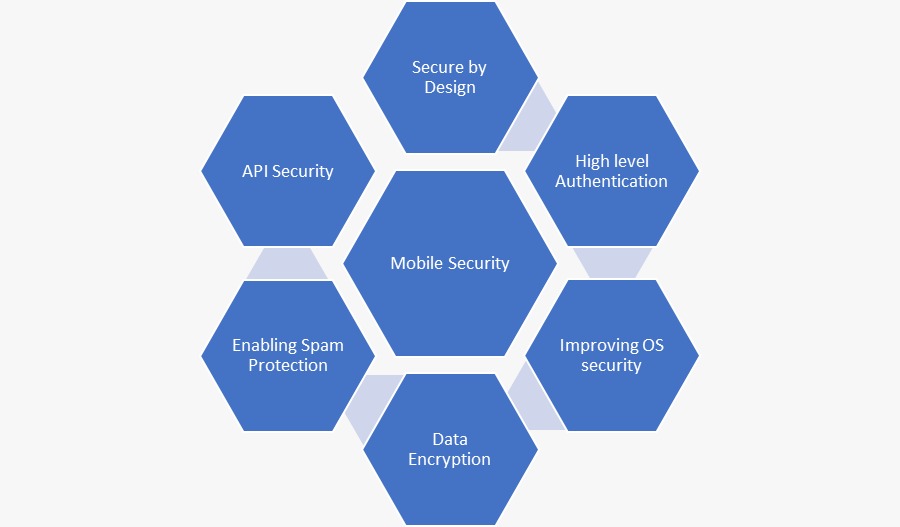
Secure by Design: One of the best approaches is to integrate security measures by embedding controls in the DNA of a mobile app. We need to evaluate every possible vulnerability or weakness that a predator could exploit and affect mobile apps through a data breach or a ransomware attack. Hence, it is better to build the application by using a secure design approach.
High-level authentication: Organizations should consider enabling the right level of access to the right set of people at the development stage. Moreover, it is worth making the users change their passwords from time to time. It is also recommended to use a multi-layered authentication process to login to sensitive or critical mobile applications to avoid unauthorized external access. The lack of such authentication results in security breaches or critical security incidents.
Improving OS security: Hardening the OS makes it difficult to hack, thereby increasing application security. For example, Apple is known for making its OS opaque to hackers and predators.
Data encryption: Data transfer from end to end is highly vulnerable at multiple points along its path. At any point, predators can steal vital records, influencing the data with weak controls on mobile devices. To avoid such situations, encrypting the data in transit and at rest would help. There are many cryptography techniques now. They are grouped into shared-key cryptography and public-key cryptography algorithms. Depending on the amount of data transferred, the required security measures are applied to simplify and secure the data.
API security: API is one of the most useful tools for mobile application developers. Data from apps can be secured through APIs, and even data transfers can be made safer through SSL with 256-bit encryption.
Conclusion
When it comes to addressing mobile device security or protection, the level of security in this space is growing, and at the same time, vulnerabilities will continue to deliver a plethora of issues to face. Organizations should apply their mobile strategy diligently, making sure security controls are embedded within the app designs and development to minimize risks. It’s time to enable the right set of security controls and new ways to strengthen the security of core mobile apps against the most common security failures. The threats mobile devices are facing are real and evolving, and it is high time that an organization adopts robust security measures after understanding the evolving threat landscape.
About Kavitha Srinivasulu
Kavitha Srinivasulu is an experienced cybersecurity and data privacy leader with over 20 years of experience focused on risk advisory, data protection, and business resilience. She has demonstrated expertise in identifying and mitigating risks across ISO, NIST, SOC, CRS, GRC, RegTech, and emerging technologies, with diverse experience across corporate and strategic partners. She possesses a solid balance of domain knowledge and smart business acumen, ensuring business requirements and organizational goals are met.
Disclaimer: This article is purely based on Kavitha Srinivasulu’s personal views and not related to her company or any other customers she has worked for.
Also read: Nurturing Responsible Online Behavior in Students by Building a Culture of Digital Citizenship
Do Follow: CIO News LinkedIn Account | CIO News Facebook | CIO News Youtube | CIO News Twitter
About us:
CIO News, a proprietary of Mercadeo, produces award-winning content and resources for IT leaders across any industry through print articles and recorded video interviews on topics in the technology sector such as Digital Transformation, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Cloud, Robotics, Cyber-security, Data, Analytics, SOC, SASE, among other technology topics.






