Whether the bank is small or big, regulatory compliance is the key to success in the future.
This is an exclusive article series conducted by the Editor Team of CIO News with Kavitha Srinivasulu, Global Head – Cyber Risk & Data Privacy: R&C BFSI at TCS.
The need to comply with regulations is rising day by day, and they play an essential aspect of any business operation, particularly in the banking and financial industry. Regulatory compliance is critical to an organization because it ensures that businesses operate within the data privacy regulations and legal framework and adhere to industry data security standards. It refers to the process of ensuring that a business adheres to the laws and regulations governing its operations. It’s no surprise that the banking industry is highly regulated, and these regulations usually align with the dynamic nature of changing regulatory requirements from time to time. Financial stability in this changing atmosphere is a crucial aspect of any economy, as it ensures the smooth functioning of financial markets and organizations.
Complying with regulatory requirements plays a significant role in protecting consumers and investors data from fraud, mismanagement, and other data exploitation. It also helps the financial industry maintain the competence and stability of its financial system controls. Failure to comply with regulations can result in significant fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage, which the banking and financial services industries are not ready to take.
There are several regulatory bodies that oversee the financial industry, including the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) in the UK and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the US. These bodies are responsible for setting regulations and imposing compliance in their respective jurisdictions. Regulators carry out regular reviews and extensive audits to ensure that businesses comply with the required or borne regulations.
Why do we need to comply with regulatory requirements?
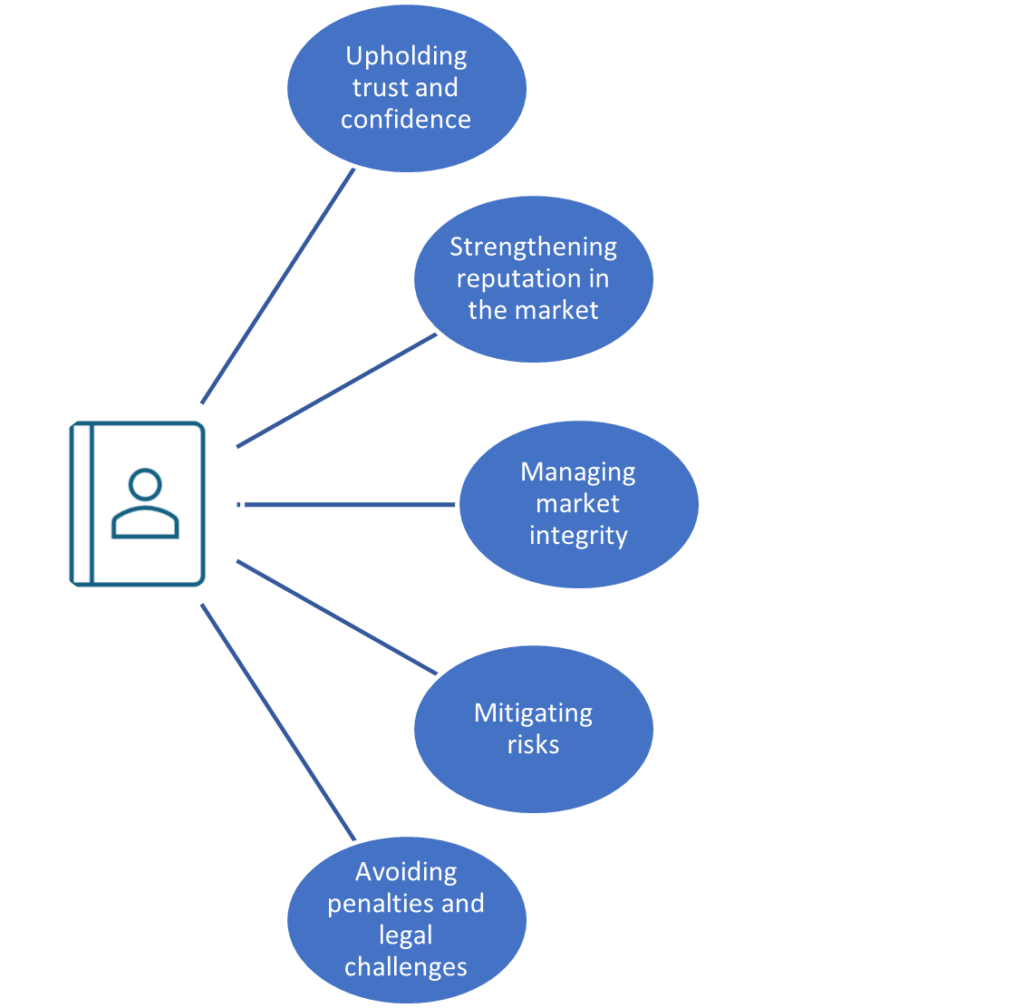
In today’s world, banking and financial institutions play a vital role in our daily lives. A huge amount of confidential information about customers is managed by financial institutions. As a result, they are subject to complying with a range of key regulations to ensure that they operate in a secure and transparent environment.
Meeting banking and financial data privacy regulatory requirements can help the organization to:
- Enhance data protection.
- Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Have a better understanding of deployed cybersecurity tools and practices.
- Management of valuable information with the right set of security controls.
- Preventing fraud and unauthorized practices in banking.
- Enhancing cybersecurity measures to protect customers data.
- Respond to cybersecurity incidents in a timely manner.
Not complying with data privacy regulatory requirements can lead to:
- Data leakage and data exploitation
- Operational disruptions.
- Losing customer tolerance.
- Reputational damage
- Legitimate legal challenges.
- Fines for non-compliance.
Some of the key activities and initiatives that financial institutions must practice to protect their data and comply with key regulations are as follows:
- Establishing a Regulatory Compliance Culture
Organizations should establish a culture of regulatory compliance by building a core governance structure aligned to privacy, legal, and security standard requirements to ensure there is a defined process in place to comply with regulatory requirements. Providing regular training and awareness programs and setting clear expectations for compliance with regulatory requirements are keys to business resilience.
- Risk Assessment
The primary step is to understand the needs of the environment and evaluate the risks and impacts on business operations. This involves evaluating the likelihood of the risk occurring and the potential impact on the organization’s operations, reputation, and financial stability using a risk assessment.
- Identifying and Mitigating Risks
It involves identifying potential risks that could arise from non-compliance with regulatory requirements and taking measures to mitigate them. The process involves identifying risks, assessing their impact, and implementing controls to mitigate them.
- Automate regulatory compliance requirements.
A compliance management tool or application can be implemented to automate compliance processes that help reduce errors and improve efficiency.
- Connecting with Regulators
Connecting with regulators on an ongoing basis can help organizations stay up-to-date with regulatory requirements and ensure that they are implementing best practices for complying with regulatory requirements in a timely manner.
The world of finance has been in constant change over the past few years with emerging technologies and changing regulatory dimensions. Regulators have been taking lots of initiatives and closely inspecting the task of ensuring financial stability while also keeping up with the changing times.
The future of regulatory compliance and financial stability is complex and multifaceted. The needs of regulators have been changing in recent times to keep a close tab on emerging risks, evolving changes, and changing technologies. Some of the key expectations from the regulators in the near future are:
- To navigate the complex regulatory landscape in a more organized and effective manner.
- There is a growing need for international regulatory cooperation.
- The role of artificial intelligence in regulatory compliance is rising to revolutionize regulatory compliance and increase transparency.
- Risk-based regulation is one approach that seeks to find this balance.
- Stringent action items and penalties for non-compliance are increasing.
- Automating regulatory compliance to centralize efforts, ensure timely actions, and reduce human interventions.
As technology continues to advance, customer expectations are changing, and new regulations are being introduced. Financial institutions must stay ahead of the curve with these dynamic changes to remain focused and data-driven. Whether the bank is small or big, regulatory compliance is the key to success in the future. The regulatory environment is constantly changing across the globe, and banks must be vigilant to ensure that they are compliant with all applicable laws and regulations. With emerging trends and technologies, banks must invest in building a robust security culture aligned with applicable regulations and legal requirements, embrace the latest technologies, automate their efforts, enable the right defense model, and ensure ongoing training and monitoring. This is the key to staying compliant with legal and regulatory requirements.
About Kavitha Srinivasulu:
Experienced cybersecurity and data privacy leader with overall 20+ years of experience focused on risk advisory, data protection, and business resilience. Demonstrated expertise in identifying and mitigating risks across ISO, NIST, SOC, CRS, GRC, RegTech, and emerging technologies, with diverse experience across corporate and strategic partners. Possess a solid balance of domain knowledge and smart business acumen, ensuring business requirements and organizational goals are met.
Do Follow: CIO News LinkedIn Account | CIO News Facebook | CIO News Youtube | CIO News Twitter
About us:
CIO News, a proprietary of Mercadeo, produces award-winning content and resources for IT leaders across any industry through print articles and recorded video interviews on topics in the technology sector such as Digital Transformation, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Cloud, Robotics, Cyber-security, Data, Analytics, SOC, SASE, among other technology topics.






