The Metaverse is boundless and there are no barriers between the physical and digital worlds
This is an exclusive interview conducted by the Editor Team of CIO News with Sunil David, Advisor at TagBox, on Metaverse
What is the Metaverse?
The Metaverse is a concept of a 3D digital world and an evolution of the Internet into a more immersive, spatial, and frictionless Web accessed by Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) headsets along with traditional computing devices like the PCs and smart phones we all use. It consists of immersive 3D virtual spaces that you can explore using a digital avatar that you can create for yourself. One can embed and link immersive content, inform and engage, tell stories, play games, go shopping, hang out with friends at a virtual coffee shop, work and collaborate with colleagues in a virtual office, and much more. The Metaverse is a world for social experiences where you can create social links with other users and AI powered virtual users, creating events that are meant to be shared together.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also accelerated the interest in building and developing Metaverses for various use cases and applications. There is now an increased demand for more interactive and immersive ways to connect with colleagues and friends as more people have started working remotely. The number of virtual 3D spaces that let co-workers join meetings, catch up, and collaborate is increasing by the day. The Microsoft Mesh platform that was unveiled in November 2021 is a very good example. It features immersive spaces for users to mingle and collaborate using their digital avatars, making remote team meetings and conferences more engaging and fun.

The Metaverse is boundless and there are no barriers between the physical and digital worlds. It is decentralised as no single entity has any control over the Metaverse. Block-chain technology provides a decentralised and transparent solution for digital proof of ownership, transfer of value, governance, accessibility, and interoperability. Crypto-currencies like Ethereum, etc., enable users to transfer value while they socialise and work in the 3D digital world. In the future, crypto currencies can potentially incentivize more people to actually work in the Metaverse. Given the trend that we are seeing today of a hybrid work environment with more companies taking their offices online for remote working, we might see Metaverse-related jobs being offered in the future.
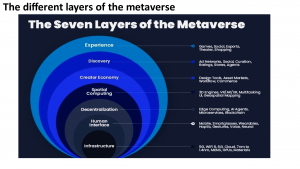
Jon Radoff, CEO of Beamable, a Live Game Services platform and a prominent industry commentator on this topic, sees the Metaverse as composed of seven layers:
Experience:
The Experience layer is where users in the Metaverse can engage in multiple ways: gaming, socialising, shopping, watching a concert, or collaborating with colleagues. When you are able to provide such immersive experiences to users, it is bound to create a lot more engagement with the platform, providing a lot of monetizing opportunities for the various stakeholders.
Discovery:
The discovery layer is about the push and pulls factors that introduce people to new and rich immersive experiences. Most discovery systems can be classified as either inbound, where the person is actively seeking information about a particular experience, or outbound (marketing that was not requested by the person, even if they had voluntarily opted in). The discovery layer could include personalised and curated portals, online agents, and advertising networks that entice users to discover and explore various areas of the Metaverse.
Creator Economy:
Not only are Metaverse experiences becoming more immersive, social, engaging, and real-time, but the number of creators who are crafting them is also increasing significantly, and we are seeing exponential growth of such creators. This layer contains all of the technology that creators use daily to create and curate the experiences that people can enjoy.
Spatial Computing:
Spatial computing has exploded into a very large category of immersive technologies that enable us to enter into and manipulate 3D spaces, and to augment the real world with more information and richer experiences. The key aspects of such software include: 3D engines to display animation and geometry; geospatial mapping; gesture and voice recognition; integration of data from multiple devices, including IOT sensors and biometrics from people; and the next generation of user interfaces.
Decentralisation:
The ideal structure of the metaverse is complete decentralisation. Experimentation and growth can increase significantly when the number of options available is maximised, ensuring interoperable systems are built within competitive markets. Distributed computing is powered by powerful cloud servers with huge compute and storage capacity, and Microservices architecture provides a very scalable ecosystem for the developer community to tap into online capabilities without the need to focus on building or integrating back-end capabilities.
In the context of decentralisation, it is important to bring in the dimension of Web 3.0. Web3 is the decentralised internet, based on distributed ledger technologies such as Block chain and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO) rather than being centralised on servers and server farms owned by organizations, individuals, or societies. Web 3.0 will be the third major evolution of the Internet after the worldwide web (Web 1.0) and the user-generated web (Web 2.0). The technology that has been used to build Web 3.0, which includes Block-chain, and Block-chain-based crypto-currencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin, and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) that are stored on a Block-chain, all have massive implications for the way we will make use of the immersive and virtual worlds of the Metaverse for work, play, socializing, and learning. NFTs are cryptographic tokens running on a block-chain that cannot be replicated. They can represent real world assets like artwork, video and music, photographs, real estate, etc. By tokenising these tangible assets, it makes buying, selling and trading them more efficient, reducing the probability of fraud and deceit.
Human interface:
Computer devices are moving closer to our bodies in ways never seen or imagined before. Smartphones have evolved significantly from the early nineties. With the advancement of technology, we are likely to see further miniaturisation, the appropriate sensors that will come at a much lower cost, the embedding and fusing of AI technology, and very low-latency access to powerful edge devices. They will absorb more experiences and applications from the Metaverse. Dedicated AR/VR hardware is also coming into the market, and in the coming years will likely evolve significantly, so we hope to see the cost of these headsets come down, making them more affordable. Beyond smart glasses, there is a growing industry that is experimenting with new ways to bring us closer to our machines, such as 3D-printed wearables that can seamlessly integrate into clothing and fashion.
Infrastructure:
The infrastructure layer includes the relevant technology that enables the user devices, connects them to the network, and delivers the rich and immersive content. This includes chip sets, battery technology, cloud servers and storage, as well as 5G and Wi-Fi transmission. The infrastructure upgrades in compute, connectivity, and storage powered by AI should significantly improve bandwidth capacity while reducing network latency, with a clear path to 6G in order to increase speeds by a huge order of magnitude.
Metaverse impact on Consumers
Purely from a consumer standpoint, the specific areas where Metaverse will power new uses cases are gaming, entertainment, and social media.
Video games are expected to play a key role in the Metaverse as they have already been built on immersive experiences with 3D graphics, VR-enabled titles, and the required platforms for user creativity and custom-built-out digital goods for use in gaming. The overall market is growing exponentially and is now at 3 billion users and is projected to reach 4.5 billion by 2030, as per a Credit Suisse report. Gaming platforms can be further unleashed within the Metaverse by allowing a gamer to be embodied and move around in the game, giving the user a completely immersive experience. As computing power rises, deeper multi-player gaming can be fully enabled and, eventually, a user could turn into a 3D hologram to show up visually with someone in another location.
The entertainment industry’s 3D virtual option for film, television, and music content is now available. New forms of entertainment are being stimulated by the Metaverse and technology has advanced to a stage where a user can be viewed as a hologram in another place and is teleported into a remote musical concert or to any social gathering. Over the last couple of years, a number of platforms have developed the major use case of virtual concerts that take the place of live performances. The benefits of these concerts are that they could reach far more users across the world than a live venue and could also transform the singer into a digital avatar or the stage into an immersive virtual environment, with high-tech special effects and opportunities for fan interaction.
Social media is embracing the Metaverse as a way to expand connectivity with the use of AR and VR to enhance user engagement. In a Metaverse-powered 3D virtual space, people can come together to interact, engage, transact, and build upon a digital version of life.
A low latency environment is required for users to feel as immersed in the Metaverse as they would in the real world. This is especially true of Motion to Photon (MTP) latency – that is, the time it takes for the user’s action to be reflected on the display screen of their device. End user interaction and engagement with holographic augmentations seamlessly requires MTP latency to be below the human perceptible limits. For example, in the registration process of AR, higher latency often results in virtual objects lagging behind the intended position, which may cause dizziness and sickness. While current cloud distribution can deliver network latency of less than 100ms, telecom networks must meet a 20ms latency to prevent users from feeling ill. Currently, last mile access is still the latency bottleneck in 4G networks. 5G, with a promise of a latency of less than 5 milliseconds coupled with Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), is expected to significantly enhance the Metaverse user experience. While 5G will be able to support the Metaverse ecosystem, the emergence of 6G in the future is likely to enhance Metaverse use cases. At the end of the day, it is superior user experience that will count, and with 6G promising 1 microsecond latency, the opportunities for players in the Metaverse to monetise will be huge.
Enterprise use cases
The applications of Metaverse hold significant potential across industries. From an industry standpoint, Metaverse can also be seen developing virtual, interactive, and immersive work environments with the help of a hybrid of virtual reality and mixed reality environments with digital avatars that offer a meaningful, engaging, and productive workplace experience. While enterprises today focus on trying to improve customer experience, what is equally important is enhancing employee experience, and Metaverse can enable such possibilities.
In the healthcare industry, Metaverse can be applicable across diverse areas, including holographic medical imaging or enabling real-time interactions between patients and healthcare professionals and care givers, irrespective of geographical boundaries, as well as creating virtual reality simulations for engaging, immersive and comprehensive learning experiences for medical students.
The Education industry can significantly benefit from the Metaverse.
Education took a 2D step through online learning during the last 2 years of the pandemic but often struggled with student engagement. Upgradation to use 3D features and VR has the potential to enhance the experience and engagement by allowing teachers and professors to teleport their students to a different place or time, or into a virtual and immersive classroom or library with their fellow students. A VR headset or glasses could enable much more active exploration of biology, history, a visit to a museum in any part of the world, or an interactive class with other students.
Impact on the Manufacturing Industry:
The Metaverse can help significantly improve the manufacturing process, particularly in the areas of product design and development, by facilitating an improved relationship and interaction between the key stakeholders—business owners, suppliers (including design companies), and the end customers. A platform like the Metaverse can result in faster production process design, an increase in the number of product designs, more collaborative and coordinated product development, and potentially reduced quality control risk, all of which will go a long way toward ensuring high quality products are designed and developed. Apart from this, customers in the Metaverse could have much better and improved visibility into the supply chain process with 3D representations of how products are designed, built, distributed, and sold. There could also be massive opportunities for manufacturers to have add-on digital products fused with IOT sensors (clothes/fashion, homes/machines etc.) in the Metaverse that can resemble, simulate, and mimic real-world products.
Metaverse concerns
There are a lot of concerns regarding Metaverse Technology and what kind of legal implications it might have. From the issue of the groping of a female digital avatar to the selling of assets in millions using cryptos, the Metaverse has thrown open a number of challenges. At the same time, this is just the beginning of the revolution of the internet, and the full implications of the technology of the Metaverse will be seen only in the next 10 years. However, policymakers and lawmakers will have to be active in ensuring that the technology of the Metaverse is in perfect sync with the current norms of data protection and privacy. This definitely calls for an early draught of the law and policy framework for the Metaverse so that technology can also evolve with the boundaries set by law.
The Metaverse is an attempt to increase the overlap and convergence of our social and digital lives in areas such as socializing, productivity, and prosperity through the use of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in online communities. However, the pursuit of this raises concerns around already contentious issues such as data security, application of anti-trust and competition laws, infringements of intellectual property rights (IPR), enforcement of liability and jurisdictional concerns, all of which must be addressed to fully appreciate the potential of the technology.
Also read: I wanted to be a tech-savvy IT professional and to lead the organisation that I will work for
Do Follow: CIO News LinkedIn Account | CIO News Facebook | CIO News Youtube | CIO News Twitter
About us:
CIO News, a proprietary of Mercadeo, produces award-winning content and resources for IT leaders across any industry through print articles and recorded video interviews on topics in the technology sector such as Digital Transformation, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Cloud, Robotics, Cyber-security, Data, Analytics, SOC, SASE, among other technology topics






